AWS Application Signals for Node.js Lambda with CDK
How to configure AWS CloudWatch Application Signals centrally for an AWS account and for individual Node.js Lambdas using the AWS CDK.
Update 2025-06-18: Provisioning with CloudFormation
It can now also be configured using CloudFormation. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/TemplateReference/aws-resource-applicationsignals-discovery.html
import { CfnDiscovery } from "aws-cdk-lib/aws-applicationsignals";
new CfnDiscovery(this, "ApplicationSignalsDiscovery");NOTE With the
CfnDiscoveryresource now available, the following sections detailing the custom resource implementation are for informational purposes only. They show the workaround that was needed before native CloudFormation support was added.
Use case
This guide shows how to use AWS CloudWatch Application Signals for your Node.js Lambda functions when using the AWS CDK for Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
Setup
In a new AWS account, the Management Console shows two steps to set up CloudWatch Application Signals. Step 1 is an account-wide setup. Step 2 is necessary for each Lambda function.
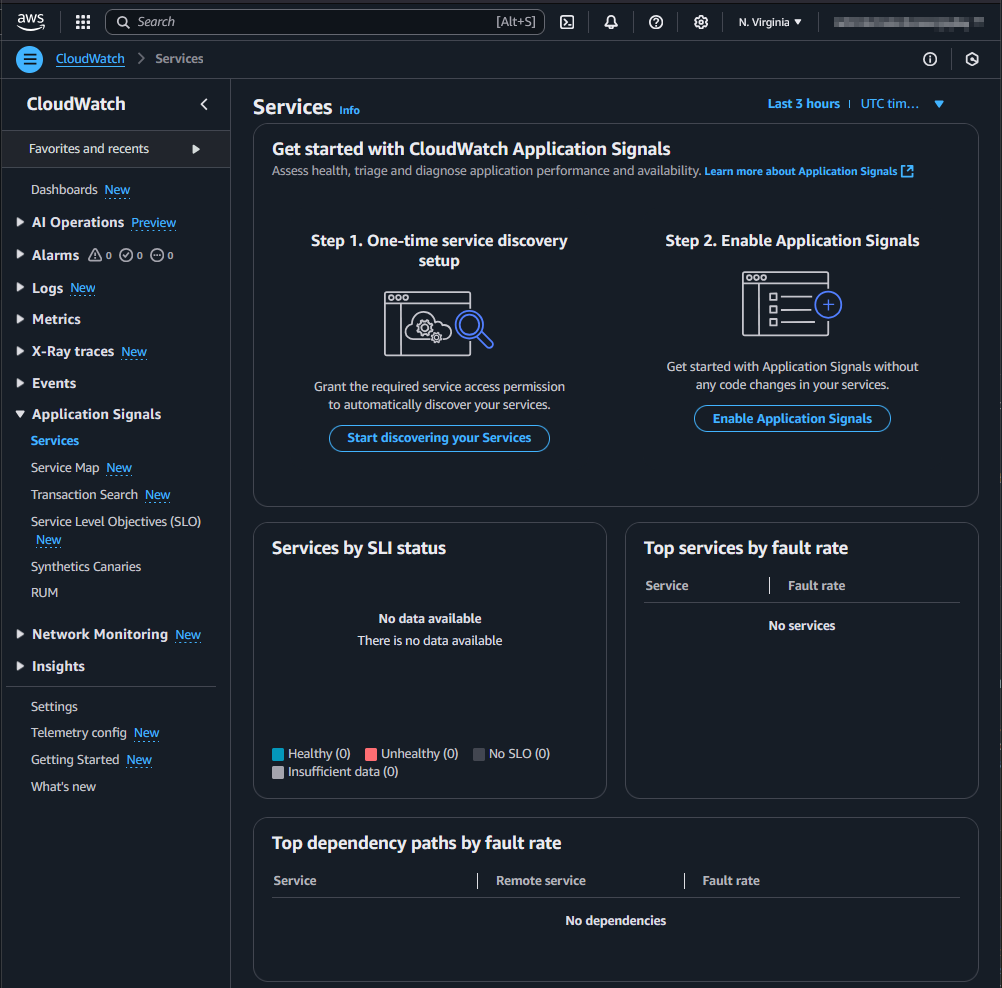
Account-wide setup
To start discovery, the service-linked role application-signals.cloudwatch.amazonaws.com must be created: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/monitoring/using-service-linked-roles.html#service-linked-role-signals.
The AWS CDK does not have a high-level construct for this. However, we can use the AWS SDK via a custom resource to achieve this.
const serviceLinkeRoleArnApplicationSignals = `arn:aws:iam::${Stack.of(this).account}:role/aws-service-role/application-signals.cloudwatch.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForCloudWatchApplicationSignals`;
const applicationSignalsStartDiscovery = new AwsCustomResource(
this,
"ApplicationSignalsStartDiscovery",
{
onCreate: {
service: "@aws-sdk/client-application-signals",
action: "StartDiscovery",
physicalResourceId: PhysicalResourceId.of(
"ApplicationSignalsStartDiscovery",
),
},
// fromSdkCalls didn't work, that's why the policy is set manually
// policy: AwsCustomResourcePolicy.fromSdkCalls({ resources: AwsCustomResourcePolicy.ANY_RESOURCE }),
policy: AwsCustomResourcePolicy.fromStatements([
new PolicyStatement({
effect: Effect.ALLOW,
actions: ["iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole"],
resources: [serviceLinkeRoleArnApplicationSignals],
}),
new PolicyStatement({
effect: Effect.ALLOW,
actions: ["application-signals:StartDiscovery"],
resources: ["*"],
}),
]),
},
);
const customResourceId = `AWS${AwsCustomResource.PROVIDER_FUNCTION_UUID.replaceAll("-", "")}`;
NagSuppressions.addResourceSuppressionsByPath(
Stack.of(this),
[
`/${Stack.of(this).stackName}/${customResourceId}/ServiceRole/Resource`,
`/${Stack.of(this).stackName}/${customResourceId}/Resource`,
],
[
{
id: "AwsSolutions-L1",
reason: "CDK managed lambda function",
},
{
id: "AwsSolutions-IAM4",
reason: "CDK managed policy",
},
{
id: "AwsSolutions-IAM5",
reason: "CDK managed policy",
},
],
true,
);
NagSuppressions.addResourceSuppressions(
applicationSignalsStartDiscovery,
[
{
id: "AwsSolutions-IAM5",
reason: "CDK managed policy",
},
],
true,
);Each Lambda function
As described here, each Lambda needs the environment variable AWS_LAMBDA_EXEC_WRAPPER with the value /opt/otel-instrument and the AWSOpenTelemetryDistroJs layer with the respective ARN.
const LAMBDA_APPLICATION_SIGNALS_LAYER_ARN =
"arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:615299751070:layer:AWSOpenTelemetryDistroJs:5";
const LAMBDA_APPLICATION_SIGNALS_ENV = {
AWS_LAMBDA_EXEC_WRAPPER: "/opt/otel-instrument",
};
const lambda = new NodejsFunction(this, id, {
runtime: Runtime.NODEJS_22_X,
timeout: Duration.seconds(10),
environment: props.enableApplicationSignals
? LAMBDA_APPLICATION_SIGNALS_ENV
: {},
});
lambda.role?.addManagedPolicy(
ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName(
"CloudWatchLambdaApplicationSignalsExecutionRolePolicy",
),
);
NagSuppressions.addResourceSuppressions(
lambda,
[
{
id: "AwsSolutions-IAM4",
reason: "CDK managed policy",
},
],
true,
);
const layerApplicationSignals = LayerVersion.fromLayerVersionArn(
this,
"LambdaApplicationSignalsLayer",
LAMBDA_APPLICATION_SIGNALS_LAYER_ARN,
);
lambda.addLayers(layerApplicationSignals);The Lambda function implementation can then look like this:
const handler = async (event: undefined, context: undefined) => {
console.log("lambda was called...");
return {
statusCode: 200,
body: JSON.stringify({
message: "Hello from Lambda!",
}),
};
};
module.exports = { handler };⚠️ The documentation currently recommends using CommonJS (CJS) instead of ECMAScript Modules (ESM).
For CommonJS, some details need to be considered, such as how the handler is exported: https://github.com/aws-observability/aws-otel-lambda/issues/284#issuecomment-1465465790
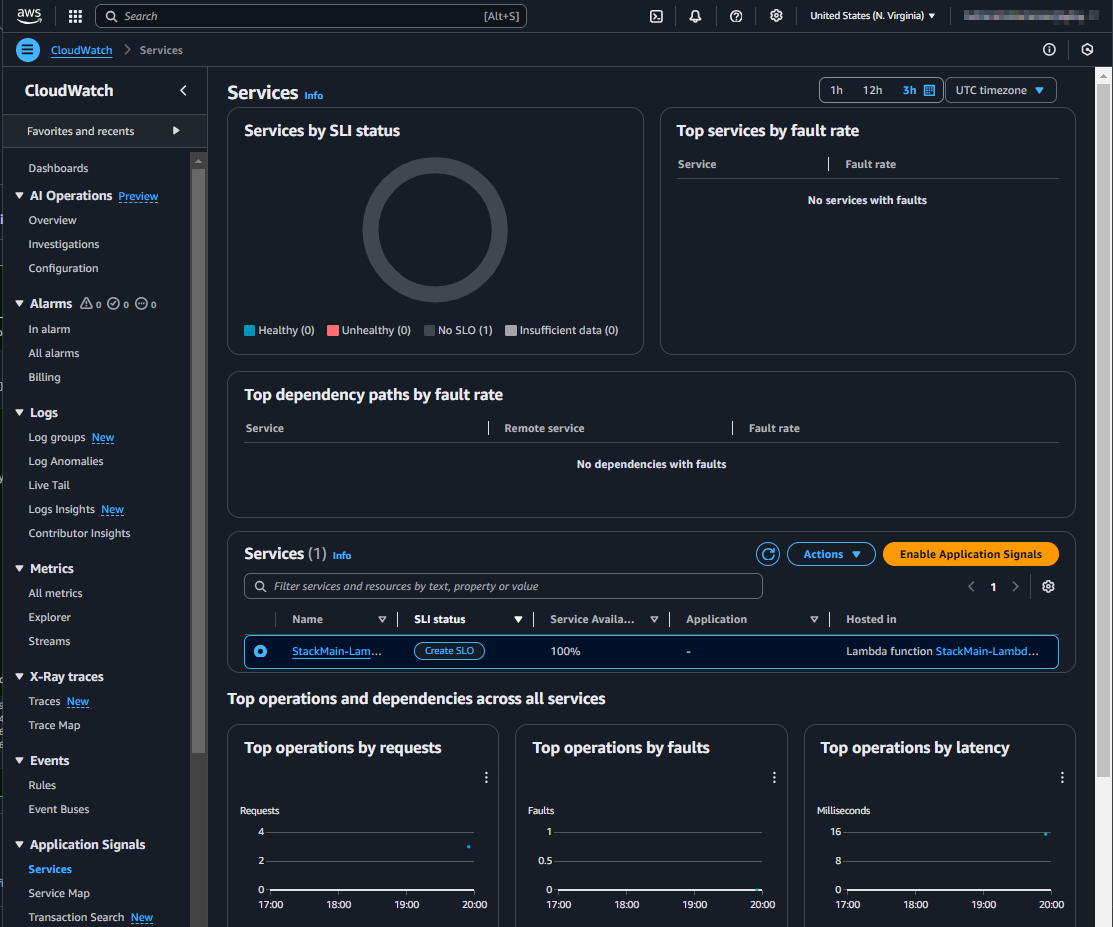
Result
After the setup and a few invocations of the Lambda function, the CloudWatch Application Signals will be visible in the Management Console. This might take a few minutes.